
A blockchain network is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof data storage and management.
Table of Contents
Blockchain have gained significant attention for their potential to revolutionize various industries, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. By using cryptographic techniques and consensus protocols, these networks ensure that data is securely stored and transactions are verified without the need for a central authority.
This technology has the potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance trust in data sharing and management. As businesses and organizations continue to explore the benefits of blockchain , it is crucial to understand their fundamental principles and potential applications in different domains.
Blockchain have revolutionized the way data is stored and transactions are conducted across various industries. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain operate on a peer-to-peer network, where each participant (or node) maintains a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency and immutability.
One of the key features of blockchain is their immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a tamper-proof record of all transactions. This feature makes blockchain particularly well-suited for applications where data integrity and security are paramount, such as financial transactions, supply chain management, and healthcare.
Blockchain utilize consensus mechanisms to validate and add new transactions to the ledger. The most common consensus mechanism is proof of work (PoW), used by networks like Bitcoin, where participants compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Other consensus mechanisms, such as proof of stake (PoS) and delegated proof of stake (DPoS), are also utilized by various blockchain, offering different trade-offs in terms of security, scalability, and energy efficiency.
Scalability is a challenge that many blockchain face as they strive to handle increasing transaction volumes. While blockchain like Bitcoin and Ethereum have faced scalability issues due to their design limitations, efforts are underway to develop solutions such as layer 2 scaling solutions, sharding, and off-chain transactions to improve scalability and throughput.
Interoperability is another important consideration for blockchain, especially as the number of networks and applications continues to grow. Interoperability allows different blockchain to communicate and share data seamlessly, enabling cross-chain transactions and the exchange of assets between different networks. Projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability protocols like Interledger are working towards achieving interoperability between blockchain.
Security is paramount in blockchain, given the decentralized and open nature of the technology. While blockchain are inherently secure due to their cryptographic principles and consensus mechanisms, they are not immune to attacks. Security vulnerabilities, such as 51% attacks, smart contract bugs, and governance issues, pose ongoing challenges for blockchain networks, requiring constant vigilance and proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Despite the challenges and complexities involved, blockchain networks hold immense promise for transforming industries and driving innovation. From enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions to revolutionizing supply chain management and decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain networks are reshaping the digital landscape and paving the way for a more transparent, secure, and efficient future.

Credit: medium.com
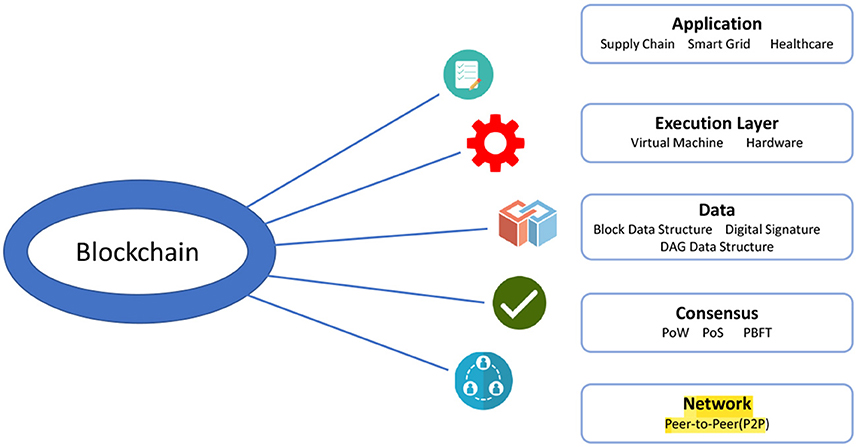
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Frequently Asked Questions For Blockchain Network
What Is A Blockchain Network?
A blockchain network is a decentralized digital ledger that records and verifies transactions across multiple computers. It enables secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. This distributed ledger technology ensures immutability, privacy, and security.
How Does A Blockchain Network Work?
In a blockchain network, transactions are grouped into blocks and then added to a chain of previous blocks. A consensus mechanism is used to validate and confirm these transactions across the network. Once a block is added, it becomes permanent and cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity of the network.
What Are The Benefits Of A Blockchain Network?
Blockchain networks offer several advantages, including enhanced security due to decentralized consensus mechanisms and cryptographic encryption. They also provide improved transparency, as all transactions are recorded and can be accessed by participants. Additionally, blockchain networks can reduce costs by eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes.
Are Blockchain Networks Only Used For Cryptocurrencies?
While blockchain networks are most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, their applications extend far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain technology can be used in various industries, such as supply chain management, healthcare, finance, and even voting systems, to ensure transparency, security, and efficiency.
Conclusion
The blockchain network revolutionizes the way we conduct transactions and ensures security through its decentralized nature. With its transparent and immutable ledger, it eliminates the need for intermediaries and promotes trust among participants. As blockchain continues to gain traction, it holds immense potential in various industries, including finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
By leveraging the power of blockchain technology, we can shape a future that is more efficient, secure, and decentralized. The possibilities are endless, and it’s exciting to see how this innovative technology will continue to evolve and transform the way we interact and transact.


